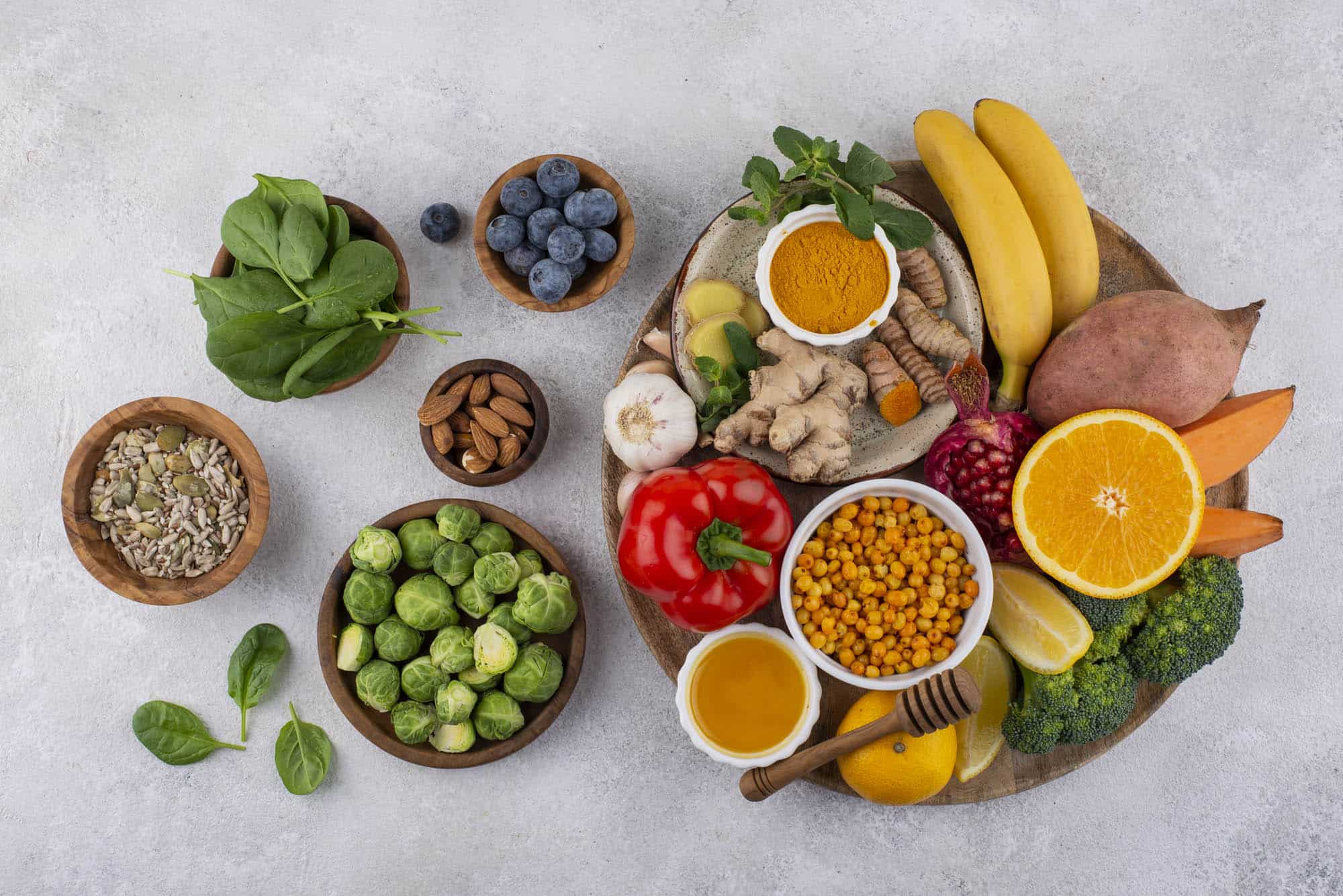
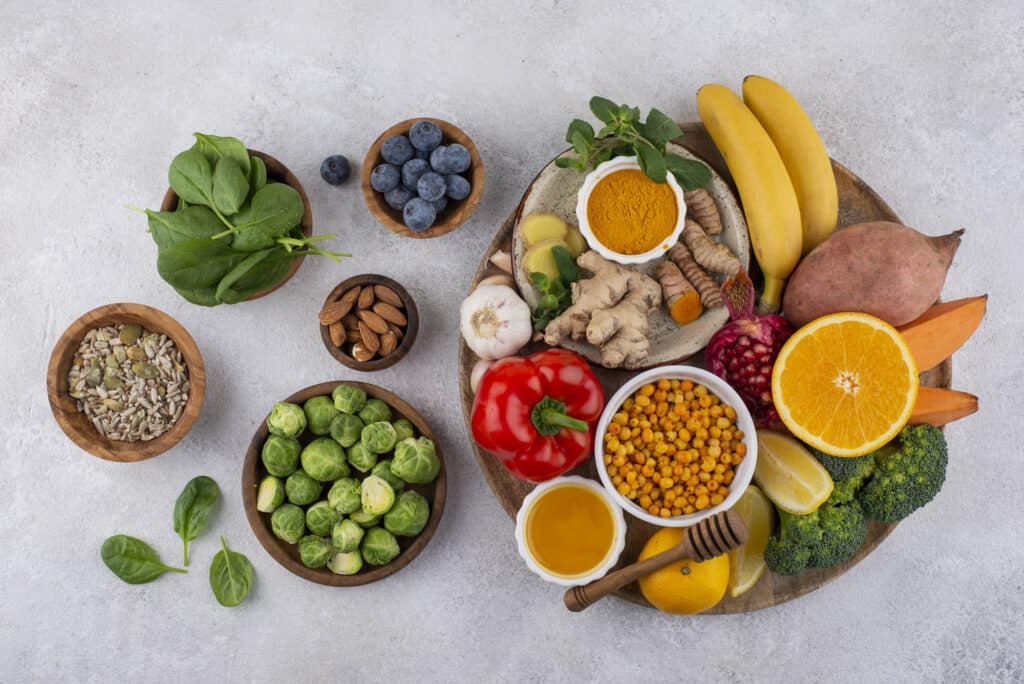
Everyone has heard that they should be eating more carrots to improve their eyesight. This is because of the high levels of beta-carotene found in carrots, which is said to be essential in maintaining healthy eyes. However, there are actually quite a few different vitamins and nutrients that play a crucial role in supporting and protecting your vision.
A well-balanced diet that includes key nutrients can help reduce the risk of eye diseases such as macular degeneration, cataracts, and dry eye syndrome. Nutritional deficiencies can contribute to poor vision, so incorporating these essential vitamins and minerals into your daily intake is vital for maintaining optimal eye health.
Here are 10 essential vitamins and nutrients that should be a part of your diet to promote healthy vision:
1. Zeaxanthin and Lutein
Zeaxanthin and lutein are powerful antioxidants that are found in high concentrations in the macula, the central part of the retina. These nutrients are known to help filter harmful blue light and protect the eyes from oxidative stress.
Sources: Leafy green vegetables (such as spinach, kale, and collard greens), eggs, corn, and orange peppers.
Benefits: Studies suggest that a diet rich in lutein and zeaxanthin may reduce the risk of progression of chronic eye diseases, such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD).The effect of these antioxidants on preventing development of this disease has yet to be determined.
2. Vitamin C
Vitamin C is an antioxidant that helps maintain the health of blood vessels in the eyes and can reduce the risk of cataract progression. It also works alongside other vitamins to slow the progression of AMD.
Sources: Citrus fruits (oranges, lemons, grapefruits), strawberries, bell peppers, and broccoli.
Benefits: Studies suggest that people who consume high levels of vitamin C may slow down cataract progression over time..
3. Vitamin E
Vitamin E is another powerful antioxidant that helps protect eye cells from free radical damage, which can lead to vision deterioration over time.
Sources: Nuts (such as almonds, walnuts, and sunflower seeds), sweet potatoes, and vegetable oils.
Benefits: Research indicates that vitamin E may slow down the progression of cataracts and AMD by neutralizing oxidative damage to the eyes.
4. Essential Fatty Acids (Omega-3s)
Omega-3 fatty acids are vital for maintaining proper eye health and retinal function. They play a crucial role in reducing inflammation and improving symptoms of dry eye.
Sources: Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, tuna, and sardines), flaxseeds, and walnuts.
Benefits: Omega-3s help maintain a healthy tear film, which is essential for preventing dry eye symptoms. They also play a role in reducing the risk of AMD and may slow its progression.
5. Zinc
Zinc is an essential mineral that helps transport vitamin A from the liver to the retina, where it plays a key role in producing melanin, a protective pigment in the eyes.
Sources: Shellfish (oysters, crab, lobster), beef, pork, eggs, and legumes (chickpeas, lentils, and beans).
Benefits: Zinc concentrations are high in the retina, and adequate intake is essential for reducing the risk of night blindness and age-related eye diseases.
6. Beta-Carotene (Vitamin A)
Beta-carotene is converted into vitamin A in the body, which is essential for maintaining good night vision and preventing dry eyes.
Sources: Carrots, sweet potatoes, pumpkins, and leafy greens.
Benefits: Vitamin A is crucial for protecting the cornea and reducing the risk of night blindness and dry eye syndrome.
7. B Vitamins (B1, B2, B6, B12, and Folate)
B vitamins are essential for reducing inflammation and lowering homocysteine levels, which are linked to an increased risk of AMD.
Sources: Whole grains, eggs, dairy products, legumes, and lean meats.
Benefits: Research suggests that B vitamins can reduce the risk of AMD and cataracts and support overall eye health by improving blood flow to the retina.
8. Copper
Copper is an essential trace mineral that plays a role in maintaining healthy nerve function, including the optic nerve.
Sources: Nuts, seeds, whole grains, and dark chocolate.
Benefits: Copper deficiency has been linked to an increased risk of optic nerve damage, so ensuring adequate intake is important for vision protection.
9. Selenium
Selenium works alongside other antioxidants to protect the eyes from oxidative damage and reduce the risk of cataracts.
Sources: Brazil nuts, seafood, eggs, and mushrooms.
Benefits: Studies suggest that selenium may help slow down cataract progression and the progression of AMD.
10. Lycopene
Lycopene is a carotenoid with strong antioxidant properties that help protect the eyes from UV damage and oxidative stress.
Sources: Tomatoes, watermelon, red peppers, and pink grapefruit.
Benefits: Lycopene has been linked to a reduced risk of cataract progression and AMD, making it a valuable nutrient for eye health.
Conclusion
A diet rich in vitamins and nutrients can significantly improve and maintain eye health. While carrots are a well-known source of vision-supporting nutrients, a well-rounded diet that includes leafy greens, citrus fruits, nuts, fish, and whole grains is essential for long-term vision protection. By incorporating these 10 essential vitamins and minerals into your diet, you can help reduce the risk of age-related eye diseases, maintain optimal retinal function, and promote overall eye health.
If you have specific concerns about your eye health, schedule an appointment with our team of eye care professionals for a comprehensive exam. You might also consider speaking with a nutritionist to develop a diet plan tailored to your individual needs. Prioritizing proper nutrition now can lead to a lifetime of healthy vision and better overall well-being.